Butter vs. Margarine (Plus 10 Healthy Fats We Love!)
When it comes to the butter aisle, picking the best product for your health can be a confusing decision that ends up leaving a lot of people stumped. It's no wonder so many people don't know whether they should be opting for butter or margarine, as years ago we were continuously told that butter was a big no-no.
This caused vegetable-oil based margarines to increase in popularity as doctors started warning patients about the dangers of saturated fats and recommending that margarine was the safer alternative for heart conditions.
We're going to stop this confusion and reveal why you should never consume vegetable oil or margarine! Aside from “healthy whole grains,” vegetable oils and margarine are some of the most misunderstood and over-recommended foods in the health community.
You’ve probably heard these referred to as “heart healthy oils,” a good alternative to those “artery clogging saturated fats.” These oils are supposed to help lower cholesterol and blood pressure, increase weight loss, and somehow improve overall health.
Only One Problem...Again, Science Doesn’t Back These Claims Up!
What Are Vegetable Oils / Margarine?
Vegetable oils (and margarine, made from these oils) are oils extracted from seeds like the rapeseed (canola oil) soybean (soybean oil), corn, sunflower, safflower, etc. They were practically non-existent in our diets until the early 1900s when new chemical processes allowed them to be extracted.
Unlike butter or coconut oil, these vegetable oils can’t be extracted just by pressing or separating naturally. They must be chemically removed, deodorized, and altered. These are some of the most chemically altered foods in our diets, yet they get promoted as healthy.
Vegetable oils are found in practically every processed food, from salad dressing to mayo to conventional nuts and seeds. These oils are some of the most harmful substances you can put into your body, but more on that in a minute!
How Vegetable Oils Are Made
Vegetable oils are manufactured in a factory, usually from genetically modified crops that have been heavily treated with pesticides.
Take for instance, the common Canola oil, the beauty queen of the vegetable oil industry. It was developed by making a hybrid version of the rapeseed, and it was given its name in the 1980s as part of a marketing effort organized by a conference on mono-saturates.
Rapeseed oil contains high amounts of the toxic erucic acid, which is poisonous to the body. Canola oil is an altered version, also called Low Erucic Acid Rapeseed (LEAR) and it is commonly genetically modified and treated with high levels of pesticides.
Canola (modified rapeseed oil) is produced by heating the rapeseed and processing with a petroleum solvent to extract the oil. Then another process of heat and addition of acid is used to remove nasty solids (wax) that occur during the first processing.
At this point, the newly created canola oil must be treated with more chemicals to improve color and separate the different parts of the oil. Finally, since the chemical process has created a harsh smelling oil, it must be chemically deodorized to be palatable.
If the vegetable oil is going to be made into shortening or margarine, is undergoes an additional process called hydrogenation to make it solid at cold temperatures. Unlike saturated fats (butter, coconut oil, etc.) vegetable oils are not naturally solid at these temperatures and must be hydrogenated to accomplish this. During this process of hydrogenation, those lovely trans fats we’ve heard so much about are created.
The chart below outlines the process:
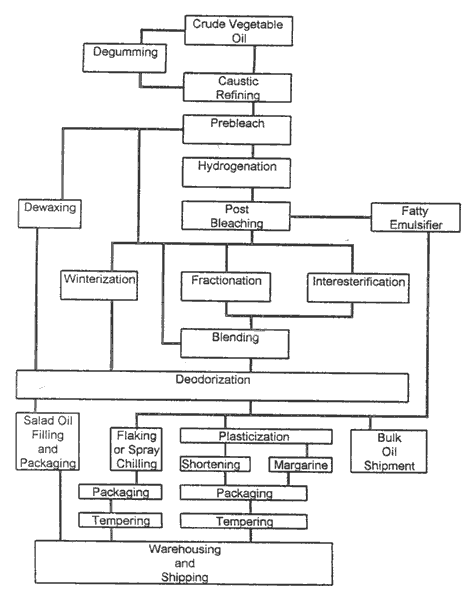
Nothing like petroleum produced, overheated, oxidized, and chemically deodorized salad dressing for dinner…. yum.
(Compare that to butter… Step 1: milk cow. Step 2: let cream separate naturally. Step 3: skim off cream. Step 4: shake until it becomes butter.)
What’s Wrong With Vegetable Oils?
There are many problems with vegetable oil consumption, and in my opinion, no amount is safe. To understand why, let’s look at a few of the biggest problems with vegetable oils:
Our Bodies Aren’t Meant To Consume Them!
The fat content of the human body is about 97% saturated and monounsaturated fat, with only 3% Polyunsaturated fats. Half of that three percent is Omega-3 fats, and that balance needs to be there. Vegetable oils contain very high levels of polyunsaturated fats, and these oils have replaced many of the saturated fats in our diets since the 1950s.
The body needs fats for rebuilding cells and hormone production, but it has to use the building blocks we give it. When we give it a high concentration of polyunsaturated fats instead of the ratios it needs, it has no choice but to incorporate these fats into our cells during cell repair and creation.
The problem is that polyunsaturated fats are highly unstable and oxidize easily in the body (if they haven’t already oxidized during processing or by light exposure while sitting on the grocery store shelf). These oxidized fats cause inflammation and mutation in cells.
In arterial cells, these mutations cause inflammation that can clog arteries. When these fats are incorporated into skin cells, their mutation causes skin cancer. (This is why people often get the most dangerous forms of skin cancer in places where they are never exposed to the sun, but that is a topic for another day!)
When these oils are incorporated into cells in reproductive tissue, some evidence suggests that this can spur problems like endometriosis and PCOS. In short, the body is made up of saturated and monounsaturated fats, and it needs these for optimal health.
Vegetable Oils Contain High Levels Of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
I’ve talked before about how the body needs Omega-3 and Omega-6 fats in balance, preferably a 1:1 ratio. Most people consume a much higher ratio of Omega-6 fats, and this can lead to problems.
Unbalanced levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 fats have been linked to skin cancer and many types of cancers. An article by the Institute For Natural Healing explains:
In one study performed at the University of Western Ontario, researchers observed the effects of ten different dietary fats ranging from most saturated to least saturated. What they found is that saturated fats produced the least number of cancers, while omega-6 polyunsaturated fats produced the most.
Numerous other studies have also shown that polyunsaturated fats stimulate cancer while saturated fat does not, and that saturated fats do not break down to form free radicals.
Chemicals And Additives In Vegetable Oils And Fats
Since vegetable oils are chemically produced, its not really surprising that they contain harmful chemicals. Most vegetable oils and their products contain BHA and BHT (Butylated Hydroxyanisole and Butylated Hydroxytoluene) which are artificial antioxidants that help prevent food from oxidizing or spoiling too quickly.
These chemicals have been shown to produce potential cancer causing compounds in the body, and have also been linked to liver/kidney damage, immune problems, infertility or sterility, high cholesterol, and behavioral problems in children.
Vegetable oils also contain residues of the pesticides and chemicals used in their growth and manufacture and most often come from genetically modified sources.
Reproductive Problems And Problems In Children Caused By Vegetable Oil Consumption
Vegetable oils are extremely damaging to the reproductive system and the developing bodies of unborn babies and children. Because the reproductive system in both men and women is constantly producing and dividing new cells, there is potential for mutation and problems when these cells are made of the wrong kind of fats and are oxidized.
This same thing applies to unborn babies and children, whose cells are dividing at high rates. There is more potential for mutation because there are more cells dividing. This article by Healing Naturally By Bee reveals:
"What the scientific literature does tell us is that low fat diets for children, or diets in which vegetable oils have been substituted for animal fats, result in failure to thrive–failure to grow tall and strong–as well as learning disabilities, susceptibility to infection and behavioral problems. Teenage girls who adhere to such a diet risk reproductive problems. If they do manage to conceive, their chances of giving birth to a low birth weight baby, or a baby with birth defects, are high."
Excess consumption of vegetable oils also causes problems with hormone production, since hormones are dependent on certain fats for their manufacture. Vegetable oils that are hardened by hydrogenation to make shortening or margarine are especially damaging.
Other Effects Of Vegetable Oils On The Body
Because vegetable oils oxidize easily, they deplete the body of antioxidants since the body must use these to attempt to neutralize the oxidation. People with high consumption of vegetable oils and their products are at risk for Vitamin E deficiency and other deficiencies.
Vegetable oil consumption has been linked to a host of other problems, among them (from the same article above):
"In test animals, diets high in polyunsaturates from vegetable oils inhibit the ability to learn, especially under conditions of stress; are toxic to the liver; compromise the integrity of the immune system; depress the mental and physical growth of infants; increase levels of uric acid in the blood; cause abnormal fatty acid profiles in the adipose tissues: have been linked to mental decline and chromosomal damage and accelerate aging. Excess consumption of polyunsaturates is associated with increasing rates of cancer, heart disease and weight gain."
In light of all that information, how do you sort out which oils are healthy, and which ones aren’t. Even more important, how do you know how much of each one to consume to be healthy?
Oils And Fats To Avoid:
Vegetable Oils and their fats should be avoided completely. There are much healthier alternatives and there is no reason or need to consume these types of fats. The main culprits to watch out for are:
- Canola Oil
- Corn Oil
- Soybean Oil
- “Vegetable” oil
- Peanut Oil
- Sunflower Oil
- Safflower Oil
- Cottonseed Oil
- Grapeseed Oil
- Margarine
- Shortening
- I Can’t Believe Its Not Butter (You better believe it!)
- Smart Balance (Not a Smart idea!)
- Any fake butter or vegetable oils products
There is no nutritional need for these oils and healthy fats can be found in higher amounts and better ratios in many other types of fats.
These foods in particular often contain one of the above unhealthy oils:
- Salad Dressings
- Store Bought Condiments
- Mayo
- Chips
- Artificial Cheeses
- Store bought nuts and snacks
- Cookies
- Crackers
- Snack Foods
- Sauces
- Practically anything sold in the middle aisles of the store
What To Do With The Vegetable Oils You Have Already?
If you already have some of the unhealthy vegetable oils in your house… don’t eat them! I’m not a fan of waste either, so use them up in other ways. They can be used to make homemade play dough or floor cleaner. You can also stick them in your shed for oiling tools. (Did I mention, don’t eat them!)
10 Healthy Fats We Love!
There are so many wonderful and healthy fats that are beneficial to the body, so there is no reason to consume the unhealthy vegetable oils above. Fats that can be consumed freely for optimal health are:
1. Coconut Oil
Filled with Medium Chain Fatty Acids and Lauric Acid, coconut oil is an all star of the saturated fats. Since the fat composition in cells in the body is largely saturated fat, it is important to get enough of it from healthy sources. Coconut oil does not oxidize easily at high temperatures or go rancid easily, making it a good choice for cooking and baking. It also makes a great natural moisturizer and can be substituted for butter.
2. Avocados and Avocado Oil
A good source of monounsaturated fats and great on salads or in guacamole. Avocado oil is milk tasting and can be used in salad dressings.
3. Olive Oil
High in monounsaturated fats and low in polyunsaturated fats, olive oil is a great oil for salad dressings, homemade mayo, and cold recipes. It shouldn’t be used for cooking since its high monounsaturated fat content makes it susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures.
4. Chia Seeds & Flaxseeds
These seeds contain a good amount of Omega-3s and are great to add to salads and smoothies! I don’t recommend flax or chia oil however, as the Omega-3 is easily corrupted by heat and oxygen and can quickly go rancid.
5. Macadamia Nut Oil & Walnut Oil
These are some of my favorite tasting oils, but it is expensive. It is great in salad dressings or mayo. It has a lot of monounsaturated fats and low levels of polyunsaturated fats.
6. Nuts
Most types of nuts (remember peanuts are not nuts) are a good source of protein and healthy fats and can be eaten in moderation without problem. Just check to make sure they haven’t been cooked in vegetable oils, which is often the case. Nuts also contain phytic acid, so consuming them in excess can be problematic for tooth and bone health unless you soak them.
And for those who choose to consume animal products then the following are recommended for their healthy fat profile:
7. Pasture Fed Cultured Dairy (Kefir, Yoghurt & Butter)
If you do consumer dairy then making sure it is organic / biodynamic, pasture fed and raw where possible is best. The cultured dairy products are by far easier to digest including yoghurt, kefir, cultured butter and cheese. When prepared in the traditional way using the best raw quality ingredients these foods can impart healthy fats including Vitamin D.
8. Pasture Raised Eggs
Another all-star in the healthy fats community, eggs are loaded with vitamins, healthy fats and necessary cholesterol. Make sure the eggs have been raised in a pastured environment so that the chickens are able to eat their natural wild diet of herbs, weeds and insects which is the basis for the rich omega-3 content in their eggs. Also, most of the beneficial fats are in the yolk and it is best kept gently cooked / under cooked.
9. Wild and Grass Fed Meats
Many meats have gotten a bad rap, and unfortunately, the animals most people eat have been as mistreated nutritionally which is one of the biggest problems. If you choose to eat meat then meats like grassfed beef and free range chicken can have a very different nutritional profile than their feedlot counterparts. Grassfed and free range meats have higher nutrient levels, healthy forms of saturated fats and even omega-3s.
10. Wild Fish
Fish are naturally high in Omega-3 fatty acids and can help improve the Omega-3/Omega-6 balance in the body. Look for sustainable wild caught sources, and stick to small fish to minimize mercury.
Are You Ready To Throw Out The Vegetable Oils? What's Your Favorite Healthy Fat Alternative?
If you haven’t already, join our free global challenge at www.GetOffTheGluten.com to receive daily recipes & health tips, access to our private group for support and inspiration, plus before and after testing to track your progress in key areas of your life such as weight, sleep, bloating, skin-conditions, mental health and more!









