This Potent Berry Is A Powerful Immune Booster!
We all know there’s no cure for the common cold. But the question remains… is there a reasonable way to help treat the symptoms of a cold?
Natural, plant-based remedies for upper respiratory infections have long been popular because they tend to be less invasive and yield fewer side effects than pharmaceutical drugs. Black elderberry is one of the most popular plant-based therapies for a cold or flu. However, just because a remedy is popular doesn’t always mean it’s actually an effective approach. In this article, we explore the biology behind the health claims associated with black elderberry.
What is Black Elderberry?
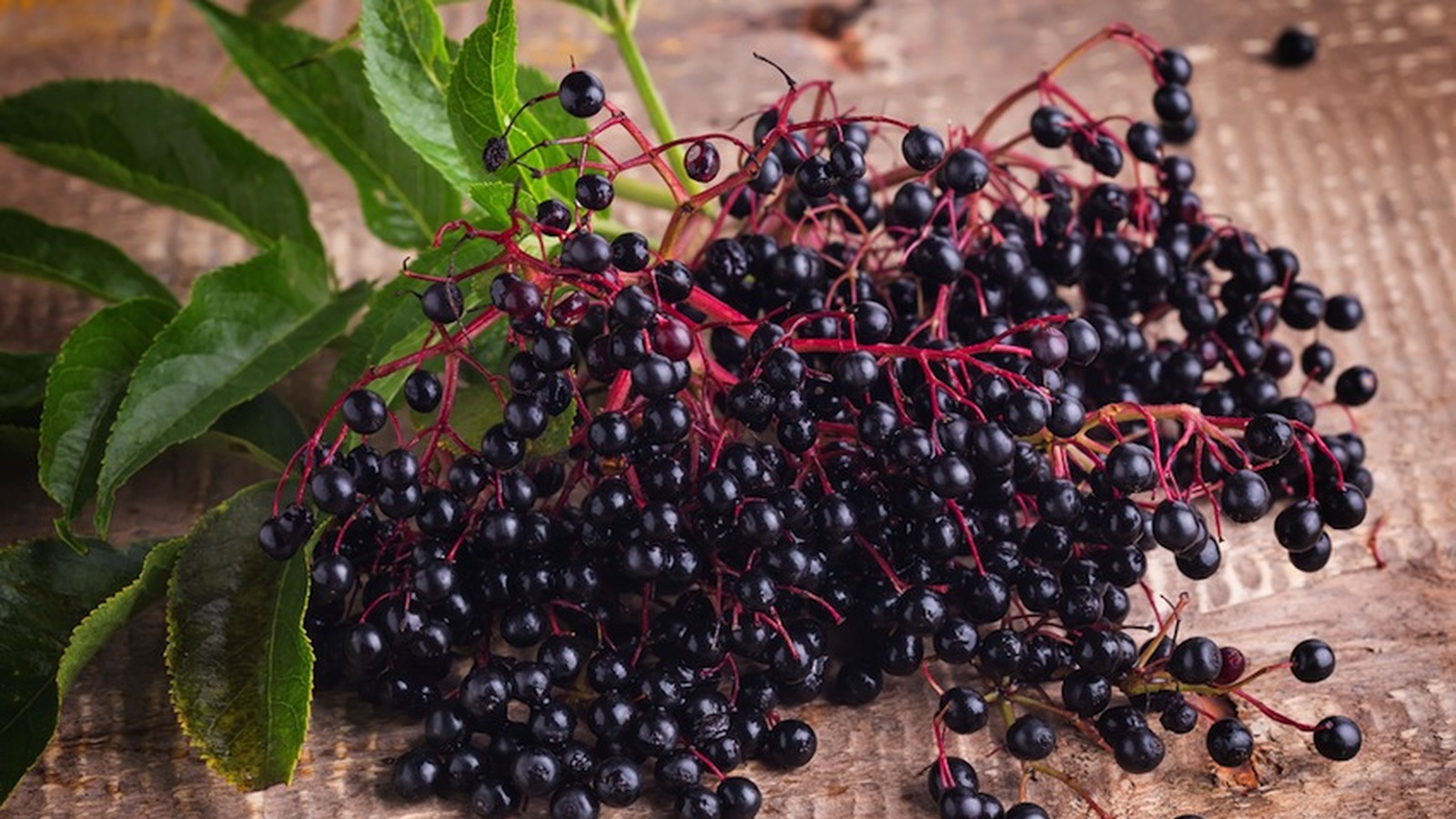
Black elderberry is a deciduous tree native to the woodlands of Europe. There are many different types of elder trees. Black elderberry, or Sambucus nigra, is the species that has become widely popular as a medicinal plant. This shrubby tree grows up to 30 feet in height and produces clusters of small, white flowers. These flowers generate green berries, which darken as the summer progresses. Both the berries and the flowers are used as medicine.
Historical Use Of Elderberry
The use of elderberry by humans is not a new concept.
Archaeologists discovered that early humans held the elderberry plant in very high regard. Gravesites from 2000 B.C. reveal that elderberry branches were buried side-by-side with the deceased. In North America, early settlers have used black elderberry for years. The berries were eaten as a sweet snack, and the strong wood was employed to build musical instruments. Native Americans were also aware of the medicinal properties of the plant. They ate the berries as a means to fend off rheumatism and viral infections.
Lately there’s been a resurgence in interest in the health benefits of this medicinal plant. Fortunately this resurgence of interest has also yielded some quality clinical and laboratory studies. These studies explore the ability of black elderberry to strengthen our immune system and thereby minimize the negative effects of a cold or flu.
Below, we’ll explore some of this published work and, in doing so, we will explain how black elderberry can help us stay healthy.
Clinical Studies Test The Ability Of Black Elderberry To Treat Colds Or Flu Infections
There are two notable clinical studies that both demonstrate the ability of black elderberry to reduce the symptoms associated with a cold or flu. One clinical trial, performed in Norway, tested 60 patients of varying ages (Zakay-Rones, 2004). All of these test subjects had just begun to feel the effect of a flu (extreme fatigue, high fever, aching body, congestion). These recently ill patients were given 15 ml of black elderberry syrup for a duration of 5 days. A similar ‘control’ group was given a placebo treatment. The scientists found that the patients who received elderberry treatment became healthy approximately 4 days earlier than the control group. The authors conclude that black elderberry treatment is ‘an efficient, safe and cost-effective treatment for influenza’.
A similar study, performed within a kibbutz community in southern Israel, also found that black elderberry extract decreased the duration of a flu by about 3-4 days. In a similar clinical design, 40 patients were administered black elderberry at the first signs of a flu. The researchers reported that approximately 90% of these patients reported a complete absence of flu-like symptoms within 3 days of beginning the elderberry treatment. This success rate was strikingly higher than the control group, which did not receive elderberry treatment (Zakay-Rones,1995).
In summary, these clinical trials demonstrate the ability of black elderberry to reduce the symptoms of a flu.
How Does Black Elderberry Work To Strengthen Our Immune System?
The primary job of our immune system is to attack and eliminate invading pathogens. In regard to a cold or flu, these invading pathogens are either a bacteria or a virus. When our bodies fight a sickness, our immune system is in battle mode. Specialized immune cells are sent out to destroy the pathogen that is making us ill. Laboratory studies have explored the manner that black elderberry syrup activates our immune system.
Below we describe how black elderberry strengthens our immune system by delivering antioxidants and by regulating our cytokine levels.
Black Elderberry Helps Regulate Our Cytokine Levels
Cytokines are small proteins that are incredibly important for our immune system. These small proteins move throughout our body and act as chemical messengers. Cytokines send signals that tell our body to either increase or decrease the intensity of an immune response. Among other things, cytokines recruit immune cells, such as macrophages, to the point of infection. These macrophage cells recognize the foreign invader (bacteria or virus) and then destroy the culprit by eating it.
When cytokine signaling is functioning properly, our body will only mount an aggressive immune response when necessary. In contrast, if there is no threat to our body, we want our cytokines to tell our immune system to take the foot off the gas. We don’t want a strong immune response happening all the time. If our immune system is overactive, then our body experiences chronic inflammation, high fevers and possibly tissue damage. We need our cytokines to help us mount an appropriate response to an infection.
Multiple laboratory studies reveal that a treatment of black elderberry can increase and regulate the cytokine levels in our immune system (Middleton, 1992; Murkovic, 2000). One especially convincing report by Barak et al., illustrates how black elderberry extract initiates a series of reactions that leads to the activation of a cluster of cytokines that are critical to our immune system (IL-6, IL-1 and TNF-alpha).
In summary, taking black elderberry when we’re sick can increase our cytokine levels, which then leads to an enhanced immune system response.
Antioxidants From Black Elderberry Help Prevent Cellular Damage
First of all… what are antioxidants? Antioxidants are small molecules that defend our cells from free radicals. Free radicals are small, charged molecules that can bang around the inside of our body and cause inflammation and cellular damage. This is why it’s a good idea to eat foods rich in antioxidants. By doing so, we help our body fend off the damage from free radicals.
Plants are a common source of antioxidants. For example, turmeric, the tropical plant from Southeast Asia, is rich in an antioxidant called curcumin. Curcumin is a powerful, bio-active compound that fights free radicals and, therefore, inhibits various forms of inflammation in our bodies. This is the reason turmeric is popular for the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Black elderberry is another plant that is rich in antioxidants. In particular, black elderberries contain molecules called flavonoids. Flavonoids are a class of antioxidants often found in leafy plants and dark-colored fruits. Various studies demonstrate that the flavonoids in black elderberries can protect cells from oxidative stress. In these experiments, living cells are exposed to damaging, oxidizing free radicals such as hydrogen peroxide, AAPH and alpha-tocopheroxyl. The authors then present data showing that the presence of flavonoids protect these cells from this free radical damage (Youdim 2000; Abuja 1998).
In summary, taking black elderberry delivers antioxidant flavonoids to our body. These flavonoids help protect our body from the damaging effects of free radicals.
When taken together, the clinical and laboratory studies discussed in this article certainly suggest that taking black elderberry is a reasonable course of action. Our immune system is bolstered by the cytokines and antioxidants derived from the black elderberry tree.
So, next time you feel a cold or flu creeping into your body, consider helping yourself out with this ancient, medicinal plant.
Discover how to lose excess fat from your belly, face & thighs in less than 7 days with this simple ancient practice. Watch the Detox Masterclass here. Playing for a limited time!